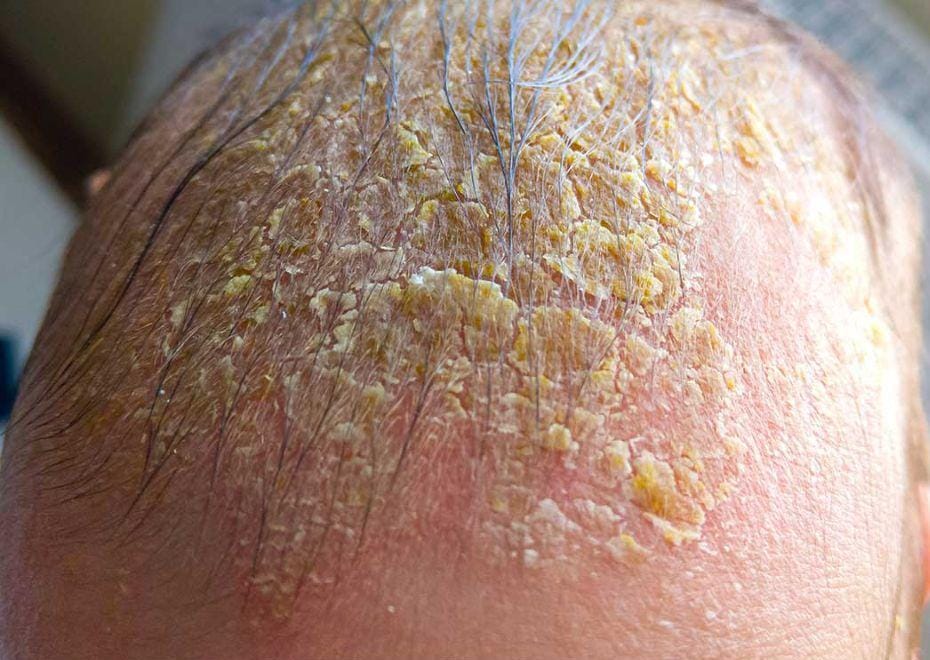
Several conditions can lead to the development of a yellow crust on the scalp. Dermatitis, such as seborrheic dermatitis, is a common cause characterized by red, flaky patches that may ooze and crust over. Psoriasis, a chronic autoimmune condition, can also lead to thickened, scaly patches on the scalp.
Infections like folliculitis or impetigo are other potential causes. Folliculitis occurs when hair follicles become inflamed, often due to bacterial or fungal infections, resulting in pustules that crust over. Impetigo, a highly contagious bacterial infection, is particularly common in children but can affect adults as well. It’s characterized by red sores that quickly rupture, ooze for a few days, and then form a yellow-brown crust.
3. Impetigo: A Common Culprit
Impetigo is a skin infection caused by either Staphylococcus aureus or Streptococcus pyogenes bacteria. It typically begins as red sores or blisters that eventually burst, leaving behind a thick, golden-yellow crust. This condition is particularly common in warm, humid environments and spreads easily through close contact.
While impetigo is more prevalent in children, adults are also susceptible, particularly those with cuts or abrasions on the skin, which provide an entry point for bacteria. Early identification and treatment are crucial to prevent the infection from spreading to other areas or individuals.
4. Symptoms to Watch For
In addition to the yellow crust, there are other symptoms to be mindful of that might indicate a more serious issue. These include persistent itching, redness, swelling, or pain around the affected area, as well as any signs of spreading or worsening of the condition.
If you experience systemic symptoms such as fever, fatigue, or swollen lymph nodes, it may signify that the infection has spread beyond the scalp and requires immediate medical attention. Documenting these symptoms can be helpful when consulting a healthcare professional.
5. When to Seek Medical Attention